Updated May 6, 2023
Difference Between Data Analyst vs Data Scientist
Data analyst vs data scientist is an important job role comparison in the analytics industry. Data analysts majorly work in data preparation and exploratory data analysis, whereas data scientists focus more on statistical models and machine learning algorithms. Data analyst professionals are generally associated with analyzing quantitative business data for business intelligence or BI implementation. And the data scientists’ role is to apply one or more machine learning algorithms to develop optimized models that help derive prescriptive and predictive analytics. The job roles and responsibilities for data analyst vs data scientist varies from organization to organization depending upon the size and type of industry.
Data Analyst
- Data Analyst examination activities can enable organizations to expand incomes, enhance operational effectiveness, advance showcasing efforts and client benefit endeavors, react rapidly to developing business sector patterns, and pick up an aggressive edge over adversaries – all with a definitive objective of boosting business execution. Contingent upon the specific application, the investigated information can comprise either authentic records or new data handled for ongoing examination employment. Furthermore, it can originate from a blend of interior frameworks and outside information sources.
- Data Analyst investigation can likewise be isolated into quantitative information examination and personal information investigation. The previous includes studying numerical information with quantifiable factors that can be measured or estimated measurably. The subjective approach is more interpretive – it centers around understanding the substance of non-numerical details like content, pictures, sound, and video, including regular expressions, topics, and perspectives.
- At the application level, BI and detailing give business administrators and other corporate laborers with significant data about crucial execution markers, business tasks, and clients, and the sky is the limit from there. Previously, information questions and reports were typically made for end clients by BI designers working in IT or for an incorporated BI group; now, associations progressively utilize self-benefit BI devices that let executives, business investigators, and operational specialists run their impromptu inquiries and fabricate reports themselves.
Data Scientist
- A Data Scientist utilizes modern investigation programs, machine learning statistics, and measurable strategies to prepare information for prescient and prescriptive displaying. Altogether, spotless and pruned information to dispose of unessential data. Investigate and look at information from various points to decide concealed shortcomings, patterns, or potential openings. Devise information-driven answers for the most squeezing challenges. Design new calculations to care for issues and manufacture new instruments to computerize work. Convey expectations and discoveries to administration and IT divisions through compelling information representations and reports that prescribe practical changes to existing methodology and systems.
- Each organization will have an alternate interpretation of employment status. Some regard their Data scientists as celebrated information investigators or join their obligations with information engineers; others require top-level examination specialists gifted in severe machine learning and information representation. As information researchers accomplish new levels of involvement or change occupations, their obligations perpetually change. For instance, a man working alone in a moderate size organization may spend a decent bit of the day in information cleaning and merging. An abnormal state worker in a business that offers information-based administrations might be requested to structure huge amounts of information that extends or make new items.
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Data Analyst and Data Scientist (Infographics)
Below are the top 5 comparisons between Data Analyst and Data Scientist:
Key Differences Between Data Analyst and Data Scientist
Let us discuss some of the major differences between a Data Analyst and Data Scientist:
- A data Analyst is a professional who analyzes the data for better reports. In contrast, Data Scientist is a research analyst to understand the data for a better data structure.
- Data Analyst skills include data visualization and statistics, whereas Data Scientist skills include programming in Python, programming in R, and other data science languages.
- Data Analyst is responsible for analyzing and visualizing the data for decision, whereas Data Scientist is responsible for algorithms and programs for understanding the data.
- Data Analyst uses data visualization, whereas Data scientists use programming.
- Data analysts solve data analysis levels, whereas data scientists solve complex data groups.
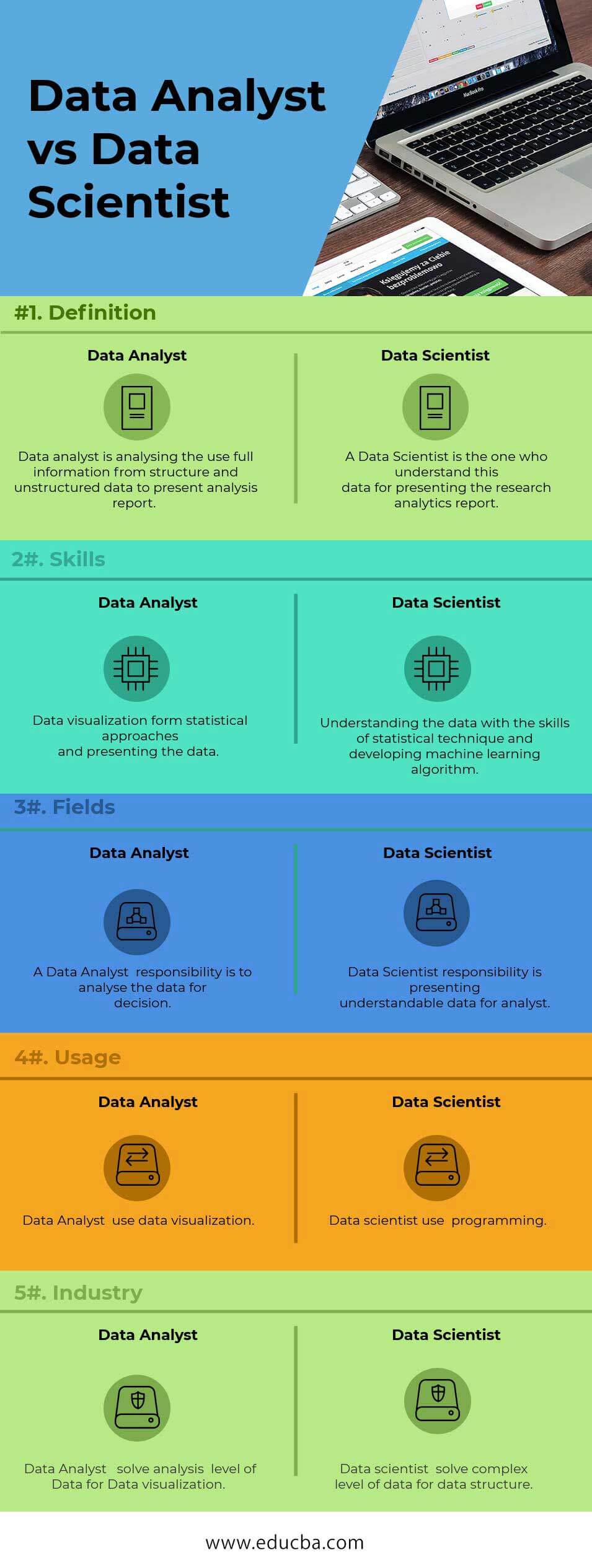
Data Analyst vs Data Scientist Comparison Table
Below are the lists of points that describe the differences between Data Analyst and Data Scientist:
| Basis of Comparisons | Data Analyst | Data Scientist |
| Definition | The Data Analyst analyzes the use of complete information from structured and unstructured data to present an analysis report. | A Data Scientist is the one who understands this data for presenting the research analytics report. |
| Skills | Data visualization forms statistical approaches and presents the data. | It is understanding the data with the skills of statistical technique and developing a machine learning algorithm. |
| Fields | A Data Analyst’s responsibility is to analyze the data for decision. | The Data Scientist’s responsibility is to present understandable data to an analyst. |
| Usage | Data Analyst uses data visualization. | Data scientists use programming. |
| Industry | Data Analyst solves analysis level of data for data visualization. | Data scientists solve complex levels of data for the data structure. |
Conclusion
In the field of Data analytics handling, the following couple of years will see us change from selective utilization of choice help frameworks to extra utilization of frameworks that settle on choices for our benefit. Especially in the field of Data Analysis examination, we are at present creating individual diagnostic answers for particular issues even though these arrangements can’t be utilized crosswise over various settings – for instance, a solution designed to distinguish inconsistencies in stock value developments can’t be utilized to comprehend the substance of pictures.
This will remain the case later on, even though AI frameworks will incorporate individual connecting segments and can subsequently deal with a more precise pattern that we would already be able to watch today. A framework that processes current information concerning securities exchanges, as well as that, additionally takes after and breaks down the improvement of political structures in light of news writings or recordings, extracts feelings from writings in sites or interpersonal organizations, screens and predicts applicable money-related markers, and so on requires the combination of a wide range of subcomponents.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Data Analyst vs Data Scientist. Here we discussed Data Analyst vs Data Scientist head-to-head comparison, key differences, infographics, and comparison table. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –