Updated June 12, 2023
Business Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers
Business Intelligence is a term that helps the user decide to run the business or important business-related questions. It allows the user to manage any organization for the growth of their business. BI helps the user to make the decision that leads to an increase in their business with the help of the relevant reports and data of any business, which is very important.
So you have finally found your dream job in Business Intelligence but are wondering how to crack the 2023 Business Intelligence Interview and what could be the probable Business Intelligence Interview Questions. Every interview is different, and the job scope is different too. Keeping this in mind, we have designed the most common Business Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers to help you get success in your interview. You can easily crack these Business Intelligence Interview Questions, which are asked in an interview.
Top 10 Business Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers
Below are the top Business Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers
Q1. What is Business Intelligence?
Answer:
The term’ Business Intelligence (BI) provides the user with data and tools to answer any decision-making important question of an organization; it can be related to running or part of a business. In short, business intelligence is used for reporting the specified data of any business, which is very important and using which higher management of any organization will decide for the growth of their business. Typically below decisions can be determined by any organization from the Business Intelligence tool:
- BI is used to determine whether a business is running as per plan.
- BI is used to identify which things are going wrong.
- BI is used to take and monitor corrective actions.
- BI is used to identify the current trends of their business.
Q2. What are the different stages and benefits of Business Intelligence?
Answer:
There are the following five stages of Business Intelligence:
- Data Source: It is about extracting data from multiple data sources.
- Data Analysis: It is about providing a proper analysis report based on practical knowledge from collecting data.
- Decision-Making Support: It is about properly using the information. It always targets to provide a proper graph on important events like take over, market changes, and poor staff performance.
- Situation Awareness: It is about filtering out irrelevant information and setting the remaining information in the context of the business and its environment.
- Risk Management: It is about discovering what corrective actions might be taken or decisions made at different times.
The following are different benefits of Business Intelligence:
- Improving decisions making.
- Speed up on decision-making.
- Optimizing internal business processes.
- Increase operational efficiency.
- Helping or driving new revenues.
- We are gaining an advantage in competitive markets with another close competitor.
Q3. What are different Business Intelligence tools available in the market?
Answer:
There are a lot of intelligence tools available in the market; below are the most popular:
- Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE)
- Cognos
- Microstrategy
- SAS Business Intelligence
- Business Object
- Tableau
- Microsoft Business Intelligence Tool
- Oracle Hyperion System
Q4. What is the universe in Business Analytics?
Answer:
The universe is a semantic layer between the database and the user interface. More correctly, it is one of the interfacing layers between the client (business user) and a data warehouse. It defines an entire relationship between various tables in a data warehouse.
Q5. Define or list the differences between OLAP and OLTP.
Answer:
In general, we can assume OLTP is helping to provide source data in a data warehouse, and OLAP helps to analyze the same.
|
OLTP System |
OLAP System |
|
| Source of Data | Operational data and OLTP are the original sources of data. | Consolidated data, OLAP data, has come from various OLTP databases. |
| Purpose of Data | For any current or fundamental business tasks. | To help with future planning, problem-solving, or decision-making. |
| Data Updating | End users initiated data frequently insert or update in the transactional database. | Data is updated based on a batch job after one defined time interval. This time can be less or more than one day. |
| Processing Speed | As usual, typically very fast. | Depends on the amount of data. After refreshing batch data, sometimes complex queries are taken more than hours. A common habit of adding an index to improve the speed. |
| Space Requirement | Again relatively small considering historical data in the archived state. | Larger as it has to hold all the historical data, aggregation structures also require more indexes than OLTP. |
| Database Architecture | Normalized data, so all the tables and data have a proper relationship. | Typically de-normalize of few tables (like factor dimensions). It usually uses a star or snowflake schema. |
| Backup and Recovery | Backup is an essential requirement on OLTP, as it’s day-to-day data, so any data loss will likely entail significant monetary loss and legal liability. | Instead of regular backups, some environments may consider simply reloading the OLTP data as a recovery method. |
Q6. What is a dashboard in a data warehouse?
Answer:
The dashboard arranges all the reports and graphs on one page. It is a collection of reports in a different format with the same functionality displayed on the same page.
Q7. Explain the difference between a data warehouse and a transnational system.
Answer:
| Transactional System | Data Warehouse System |
| It is usually designed to process day-to-day data, mainly concentrating on high-volume transaction processing rather than backend reporting. | It is usually designed to process high-volume analytical reporting and subsequence. It is also elaborating on report generation. |
| It is usually process-driven, which depends on a business-specific task or execution. | It is subject-oriented, which means it loads data from a transactional system, then opens it for any analytical reporting, which helps the organization make proper decisions based on that specific subject. |
| It usually handles current transactional data. | It usually handles historical data. |
| Transactional system data can insert, updated, or deleted in each task. | Data warehouse data is called non-volatile, meaning new data can be added regularly, but those data are rarely changed once loaded. |
| In case of performance or speed, we should always prefer a transactional system for inserting, updating, or deleting small volumes of data. | We should always prefer a data warehouse to retrieve a relatively large data volume quickly. |
Q8. Explain the Fact and Dimension table with an example.
Answer:
A Fact table is the center table in the star schema of a data warehouse. It was holding quantitative information for analysis, and at the maximum time, it de-normalized.
A dimension table is one of the important tables in a data warehouse’s star schema, which stores attributes, or dimensions, that describe the objects in a fact table.
The fact table mainly holds two types of columns. The foreign key column allows joins with dimension tables, and the significant columns contain the data that is being analyzed.
Example: Suppose one company sells products to customers. So every sale will be one fact, so the fact table holds that information like below:
| Time ID | Product ID | Customer ID | Unit Sold |
| 4 | 17 | 2 | 1 |
| 8 | 21 | 3 | 2 |
| 8 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
Now in the fact table, there has a customer id, so we need to maintain one dimension table for a customer like below:
| Customer ID | Name | Gender | Income | Education | Region |
| 1 | SS | M | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 2 | AC | M | 3 | 5 | 1 |
| 3 | MS | F | 1 | 7 | 3 |
Q9. Define or list the differences between snowflake and star schemas.
Answer:
| Snowflake Schemas | Star Schema | |
| Maintenance | No redundancy, so easier to maintain. | Holding redundant data so less easy to maintain. |
| Complexity | More complex query, hence less easy to understand. | Lower a complex query, so easy to understand. |
| Query Performance | The more foreign key, so longer the query execution time. | Less a number of foreign keys, so query execution is faster compared to a snowflake. |
| Utilization | Good to use for data warehouse core to simplify complex relationships (many: many). | Good for Data Mart with a simple relationship (1:1 or 1: many). |
| Dimension Table | A snowflake schema may have more than one dimension table for each dimension. | Star schema contains only a single-dimension table for each dimension. |
| De-normalize | A fact table is in de-normalized form, but the dimension table is in normalized form. | The fact and dimension of both the tables are in de-normalized form. |
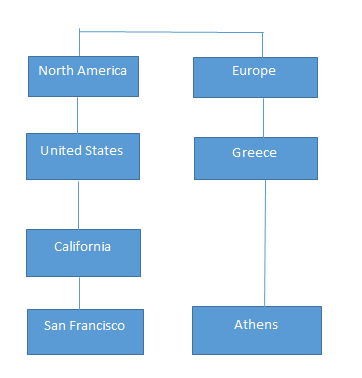
Q10. Explain or Define a RAGGED hierarchy.
Answer:
A ragged hierarchy maintains a relationship in case a parent member of at least one member of the dimension is not in the level immediately above the member. As an example, if we think about geographical hierarchy and consider North America as a continent, then it has a country (like the United States), province or state (like California), and city (like San Francisco). But if we consider Europe, Greece, or Athens, it doesn’t have this kind of hierarchy. So in this example, Europe, Greece, or Athens branches descend to a different depth, creating a ragged hierarchy.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to List of Business Intelligence Interview Questions and Answers so that the candidate can crack down on these Business Intelligence Interview Questions easily. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –