Updated June 27, 2023
Introduction to Java Commands
Java is a multi-purpose, general computer programming language that has the best amalgamation of being class-based and object-oriented. It doesn’t have a plethora of implementation dependencies too. Today, almost in every realm, we can see Java being in the picture. This language provides mainly three computing platforms viz. J2SE, J2ME, J2EE. This is one of the most popular client-server application-based programming languages with a Java Development Kit comprising of Java Runtime Environment and other utilities. It consists of Java Virtual Machine and a bytecode, making it possible for this language to get compiled and executed at any platform and any computer architecture. Java is supported by a few development environments such as Eclipse, IntelliJ, BlueJ, Netbeans, etc., but there are some basic commands which can be executed through terminal or command prompt or some syntax used in programming. In this tutorial, we are going to discuss different types of Java commands.
Basic Java Commands
The basic commands are as explained below:
- Java –version: This is one of the very basic Java commands which is used to check the version of java installed on your machine. This is also used to ensure whether the installation and the PATH setting of variables are done rightly.
- Javac –version: This command is used to tell you the compiler version, which is responsible for compiling the source code. This also is a part of the Java Development Kit, popularly known as JDK.
- Whereis: This Java command is used to find the specific component within the directory. In the below case, we have taken into consideration javac.
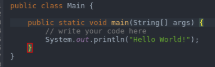
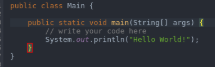
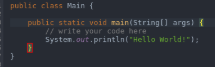
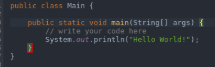
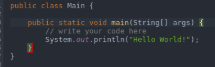
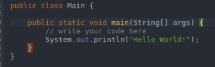
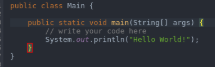
- To execute a program once it has been converted into bytecode, we make use of Java and then the program name. In the below example, we have taken the program with the name of Hello World.
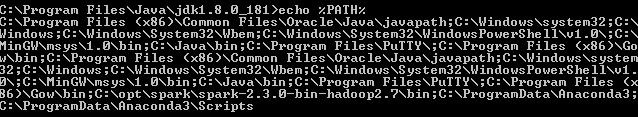
- Echo: This echo command is used in Java and is a must-know command as it helps display the data of a particular file. Generally, this is used to check the PATH variables.
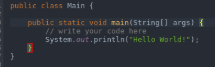
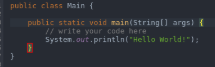
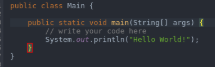
- Main: As the name suggests, this is the program’s main function where the compiler first reaches and executes the portion of it.
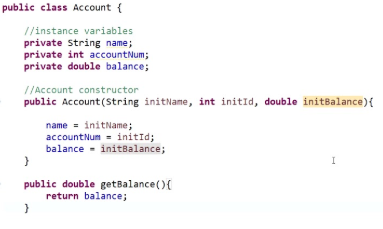
- Public: This is an access modifier in java that is used to define what level of access will the program controls would have. Public means that the class is publically available.
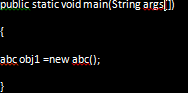
- Class: It is a logical entity and often said to be the blueprint of the object. This contains functions and other data members in a single entity called class.
- Object: Everything in Java is an object as it is the only physical entity of which everything is comprised of. It is the combination of procedures and data working on the already available data.
- Static: This is a java keyword that ensures that the method of the function block can be called without making use of an object.
Intermediate Java Commands
The intermediate commands are as explained below:
- This is the java keyword used to specify that there will be no return type possible for the intended function.
- args[]: This is used to specify the arguments contained in the main function, and the [] imply the array.
- String: This is a pre-built Java class that is used to handle all the string related and alphabets related keywords of Java.
- System: This is a pre-built class in Java present in the default lang package, which is used to handle the standard input, standard outputs, and other stream errors.
- Out: This is the object and a static member of the system class which is used to print the message on the output path, which is generally a console or a file.
- Print: This method is used to print the contents of the program in a sequential way, and the cursor would not come to the next line.
- Println: This function is used to print the contents in a new line.
- Private: This is the access modifier in java used to define the method’s scope or function within the class only.
- Int: This is the integer datatype that is used to handle all the integer type values, and therefore a variable needs to be initialized with the int datatype.
- Double: Another datatype that is used to define the variables with the decimal values. It comes under the category of Java primitive data types used for storing double-precision values. This has a long range compared to the float variable, which is also used to define and declare variables with a decimal figure.
Advanced Java Commands
The advanced commands are as explained below:
- Return: This is the command which is used at the end of the program and specifically returns only one value. It is also a reserved keyword which means it cannot be used as an identifier in Java. The return keyword can be used to exit from a method either with a value or without a value.
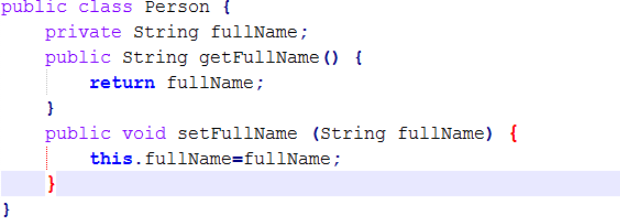
- This: This keyword in java is used to refer to the current state of the object or a current class instance variable or a current class constructor.
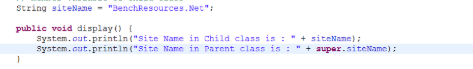
- Super keyword: It is a variable that is used to reference parent class objects or the calling of parent class methods.
- Extends: This is the keyword used in the case of inheritance, a Java object-oriented programming concept where the attributes of one component (class or an interface) are called by other components. Extends and implements go hand in hand.
Tips And Tricks to use Java Commands
When you are making use of these Java commands, using a TAB button in an IDE will fast pace your development work as the keywords will be auto-generated in this case.
Conclusion
These are some of the Java commands and keywords which Java developers can frequently use. There are several other commands which take into play along with the logic of the program. I hope you liked our article. Stay tuned.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Java Commands. Here we have discussed basic, intermediate, and advanced Java Commands and tips and tricks to use. You may also look at the following article to learn more –