Updated November 23, 2023
Economic Order Quantity Formula (Table of Contents)
- Economic Order Quantity Formula
- Economic Order Quantity Calculator
- Economic Order Quantity Formula in Excel (With Excel Template)
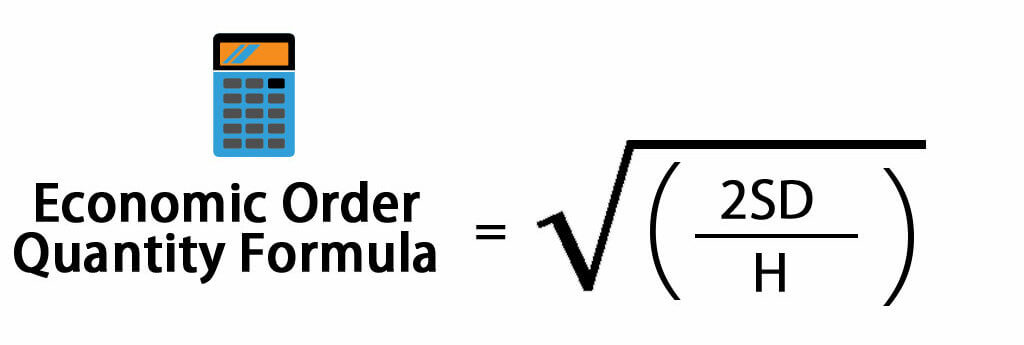
Economic Order Quantity Formula
Economic Order Quantity or EOQ can be defined as the optimum level of quantity and frequency of orders for a particular level of demand.
Here’s the Economic Order Quantity Formula –
where: –
- S: Ordering Cost or Fixed Cost
- D: Annual Quantity Demanded
- H: Holding Cost or Variable Cost
Example of Economic Order Quantity Formula
Let’s take an example to find out the Economic Order Quantity for a company: –
Economic Order Quantity Formula – Example #1
Company X has annual ordering costs of $10,000, an annual quantity demanded of 2,000, and a holding cost of $5,000.
Economic Order Quantity is Calculated as:
- Economic Order Quantity = √(2SD/H)
- EOQ = √2(10000)(2000)/5000
- EOQ = √8000
- EOQ = 89.44
Economic Order Quantity Formula – Example #2
Let’s say that Hindustan Unilever Ltd; wants to determine economic order quantity for its operations to minimize inventory costs and better cash flow management.
The annual ordering costs are Rs 10 million while the quantity demanded is 100 million. The holding costs are Rs 10 million.
Economic Order Quantity is Calculated as:
- Economic Order Quantity = √(2SD/H)
- EOQ = √2(10 million) (100 million)/10 million
- EOQ = √200
- EOQ = 14.142
Hence the ideal order size is 14.142 to meet customer demands and minimize costs. It is also the reordering point at which new inventory should be ordered.
Economic Order Quantity Formula – Example #3
Let’s say Maruti Suzuki Limited; wants to determine the economic order quantity for its operations to minimize inventory costs and better cash flow management.
The annual ordering cost is Rs 25 Crores, the quantity demanded is 1 Crore, and holding costs are Rs 10 Crore.
Economic Order Quantity is Calculated as follows:
- Economic Order Quantity = √(2SD/H)
- EOQ = √2 (25 Crore) (1 Crore)/(10 Cr0re)
- EOQ = √5
- EOQ = 2.2360
Hence the ideal order size is 2.2360 to meet customer demands and minimize costs. It is also the reordering point at which new inventory should be ordered.
Explanation of Economic Order Quantity Formula
The Economic Order Quantity helps determine the optimum level of quantity and frequency of orders for a given level of demand. We minimize the cost per order to find the best level. The key components of the EOQ formula are: –
- D: Annual Quantity Demanded
- Q: Volume per order
- S: Ordering Cost or Fixed Costs
- i: Interest rate
- C: Unit cost or variable cost
- H: Holding Cost or Variable Costs
The individual components of the Formula need to be understood before determining the Economic Order Quantity. The Economic Order Quantity is used to minimize the costs of the order. As we all know, the total costs include Fixed and Variable costs. These costs include purchase costs from the supplier or vendor, ordering, and carrying costs.
Number of orders – To determine the number of orders, divide the annual quantity demanded by the volume per order.
Number of orders = D / Q
Ordering Cost (S) – The ordering cost represents a fixed cost per unit that remains independent of the number of units ordered.
Annual Ordering Cost = Number of orders x S = D/Q x S
Holding Costs – Holding costs represent the variable costs linked to storing products in inventory. Holding costs would also be defined as opportunity costs of investing money elsewhere rather than putting it in buying inventory.
Holding Cost per Unit = i x C
Assuming constant demand, the quantity of inventory gradually depletes over time until it reaches zero. At that point, a new order is placed to replenish the inventory. To calculate the annual holding cost, you can use the following Formula:
Annual Holding Cost = Q/2 x H
Summing the annual ordering cost and annual holding cost will give us the total cost of orders annually.
Total Annual Cost (TC) = D/Q x S + Q/2 x H
To find the Economic Order Quantity, take the first derivative with respect to Q.
EOQ = dTC/dQ = √ (2SD/H)
Significance and Use
Economic Order Quantity is one of the essential tools companies use in cash flow planning for minimizing the cost of inventory or decreasing the amount of cash held up in inventory. This is because companies, particularly FMCG companies, consider inventory as their most significant asset and need to plan it appropriately to ensure sufficient inventory is available to cater to customer needs. However, the company should minimize it to achieve cost savings. The Economic Order Quantity helps in estimating that level of inventory.
Economic Order Quantity also has various other uses, one of which is estimating the reordering point or the point at which an order needs to be placed for more inventory. This is because a reorder needs to happen before inventory runs out; otherwise, it would lead to a loss of revenue for the company.
Economic Order Quantity Calculator
You can use the following Economic Order Quantity Calculator
| S | |
| D | |
| H | |
| Economic Order Quantity | |
| Economic Order Quantity | = |
|
|
Economic Order Quantity Formula in Excel (With Excel Template)
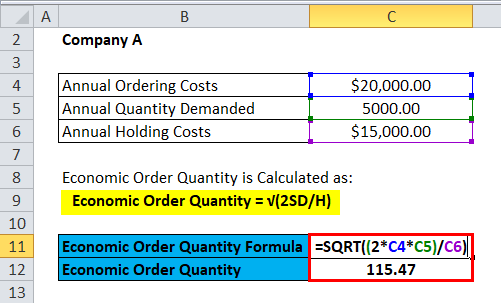
Here we will do the same example of the Economic Order Quantity formula in Excel. It is very easy and simple. You need to provide the three inputs, i.e., Ordering Cost or Fixed Cost, Annual Quantity Demanded, and Holding Cost or Variable Cost
You can easily calculate the Economic Order Quantity using the Formula in the template provided.
Conclusion
The Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) defines the optimal level of quantity and frequency of orders for a particular level of demand. Economic Order Quantity uses ordering costs and holding costs to determine the orders required. Companies utilize it in cash flow planning, minimizing the cost of inventory, and estimating a company’s reordering point.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to an Economic Order Quantity formula. Here we discuss its uses along with practical examples. We also provide an Economic Order Quantity Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –