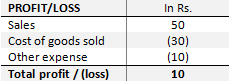Updated July 6, 2023
Difference Between Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting
Cost Accounting is a method that records and analyses the cost incurred (per unit) during the production of goods. It analyses input costs individually, at every functional stage, including production, administration, R&D, selling & distribution. Financial Accounting involves recording and analyzing a company’s financial transactions for a specific period. The company summarizes it into financial statements demonstrating its profitability or the outcome of its operations.
Cost Accounting:
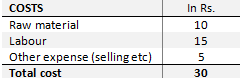
Example: Total cost of producing one unit of a pencil is Rs.30; the cost break up of various stages can be as below:
Figure 1: Cost breakdown
Financial accounting:
Example: If the same pencil is sold for Rs.50 and the cost of making a pencil and other expenses sum up to Rs.40, then the profit would be Rs.10, as below.
Figure 2: Income & expenditure
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting
Below is the top 13 difference between Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting
Key Differences Between Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting
Let us discuss some of the major differences Between Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting:
1. In cost accounting, we assess the per unit cost incurred to produce and sell products to ensure we can sell them at the appropriate price. On the other hand, financial accounting focuses on all monetary transactions to determine a firm’s profitability and financial health.
2. Cost accounting is an internal instrument for management to measure efficiency and decide on a company’s operations. On the other hand, Financial accounting prepares financial statements to show performance to the entities external to the company, like investors and creditors, etc.
- Cost accounting: Management uses it for budgeting, cost control, cost reduction, and inventory management, among others, so that it can improve margins
- Financial accounting: Knowing if the company is operating efficiently and if the money invested by outsiders will be able to generate returns or not is useful for people outside the firm.
3. Cost accounting can be allocated and recorded under various categories such as direct cost, indirect cost, fixed cost, variable cost, operating and non-operating cost, etc., whereas Financial accounting records items based on the nature of the transaction, such as income & expenditure, cash inflow, and outflow, assets and liabilities under three statements profit & loss account, cash flow statement and balance sheet respectively
4. Decisions made based on
- Cost accounting (internal):
- Whether new machinery should be bought?
- Should the old machinery be disposed of
- How costly/profitable can a new product become?
- Financial accounting (external):
- If the creditor should lend money and at what interest rate?
- Based on performance, how much should be invested in a firm?
Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting Comparison Table
Let’s look at the topmost Comparison between Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting.
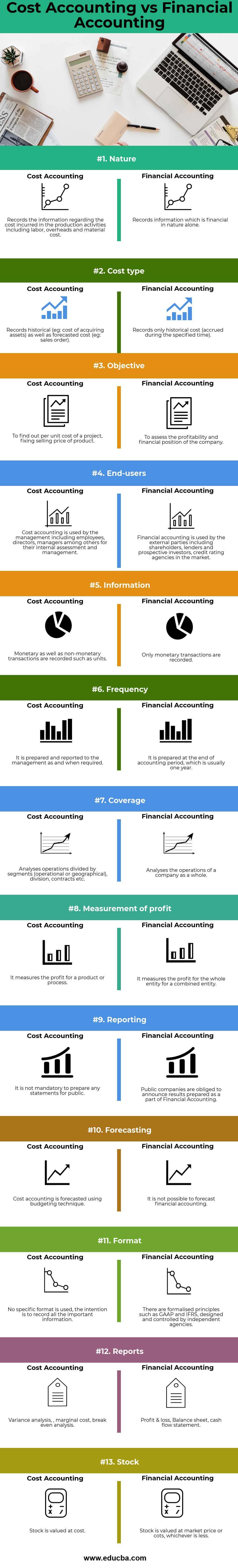
| The Basis of Comparison | Cost Accounting | Financial Accounting |
| Nature | Records the information regarding the cost incurred in the production activities, including labor, overheads, and material cost | Records information that is financial in nature alone |
| Cost-type | Records historical (eg: a cost of acquiring assets) as well as forecasted cost (eg: sales order) | Records only historical cost (accrued during the specified time) |
| Objective | To find out the per unit cost of a project, fixing the selling price of a product | To assess the profitability and financial position of the company |
| End-users | Management, including employees, directors, and managers, utilize cost accounting for internal assessment and management. | External parties utilize financial accounting, including shareholders, lenders, prospective investors, and credit rating agencies in the market. |
| Information | Financial accounting records monetary and non-monetary transactions, including units, to provide a comprehensive view of a firm’s financial performance and position. | Only records monetary transactions |
| Frequency | The management receives and reviews the prepared report as and when required. | The company prepares it at the end of the accounting period, usually one year. |
| Coverage | Analyses operations divided by segments (operational or geographical), divisions, contracts, etc. | Analyses the operations of a company as a whole |
| Measurement of profit | It measures the profit for a product or process | It measures the profit for the whole entity for a combined entity |
| Reporting | It is not mandatory to prepare any statements for public | Public companies must announce results that they prepare as part of Financial Accounting. |
| Forecasting | The budgeting technique forecasts cost accounting. | It is not possible to forecast financial accounting |
| Format | No specific format is used; the intention is to record all the important information. | Independent agencies design and control formalized principles such as GAAP and IFRS. |
| Reports | Variance analysis, marginal cost, break-even analysis | Profit & Loss, Balance sheet, cash flow statement |
| Stock | The stock is valued at the cost | The stock is valued at the lesser of the market price or cost. |
Conclusion
Cost accounting is an indirect part of financial accounting and a direct part of management accounting. Using cost and financial accounting together can reduce costs and increase a firm’s profitability.
Based on information recorded under cost and financial accounting, various analyses can be prepared, such as ratios, growth & margin trends, and industry comparison. Cost accounting information compares the cost with the revenue recorded under financial accounting. Financial accounting is required as compliance under universally defined principles, while cost accounting co-exists as a small part of the analysis.
Cost accounting identifies operational efficiencies or inefficiencies, which can be further captured under the financial statements. Both branches help make important decisions where cost accounting leads to an internal decision and directly affects the firm’s employees; financial accounting keeps the decision-making domain outside the firm, indirectly affecting employees. It is important to keep financial and operational records of a firm governed and classified under general accounting. Both branches show profitability; cost accounting does on a unit basis, and financial accounting shows in totality.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the top difference between Cost Accounting and Financial Accounting. Here we also discuss the Cost Accounting vs Financial Accounting key differences with infographics and comparison tables. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –