Updated November 3, 2023
What is a Balance Sheet?
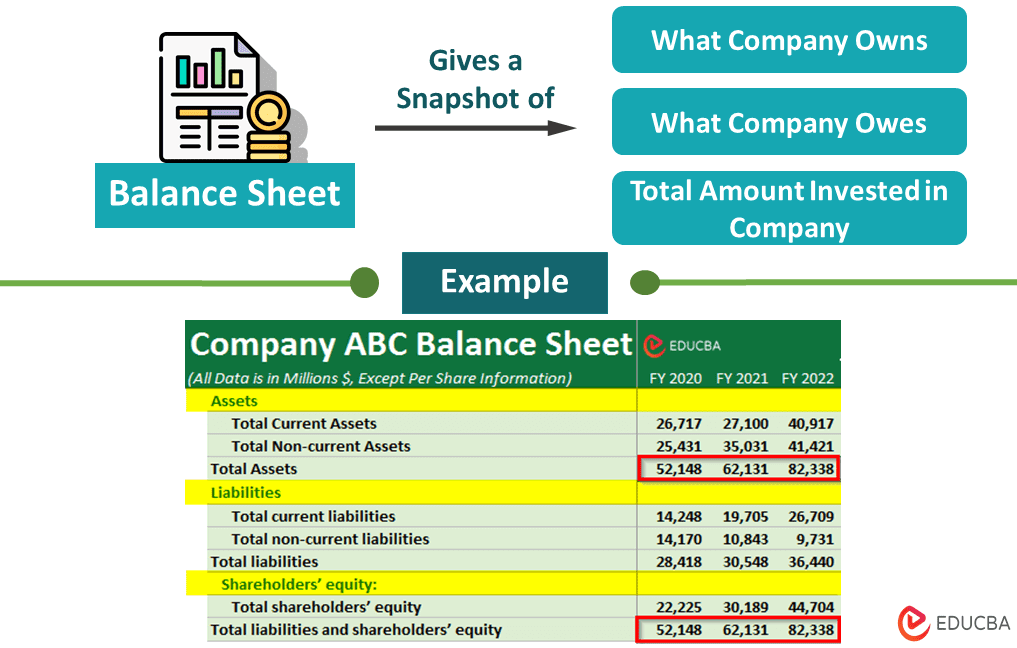
A balance sheet is a financial statement in accounting that gives us a snapshot of a business’s assets (what the company owns), liabilities (what it owes), and shareholders equity (total amount invested by its shareholders) at the end of a particular period. Companies generally prepare this financial statement at the end of a month, quarter, or year.
Also known as the statement of financial position, the balance sheet’s purpose is to report the financial position or the book value of the company’s net worth. It helps the stakeholders to quantify the company’s financial strengths as it serves as the foundation to calculate the rates of return and to evaluate the capital structure of the company. The sheet is prepared based on a principle and equation called Balance Sheet Formula.
Table of Contents
- Definition
- Format
- Components
- Real-Company Examples
- How to Construct?
- How to Read?
- Importance
- Limitations
Format
There are two formats of a balance sheet: Vertical and horizontal.
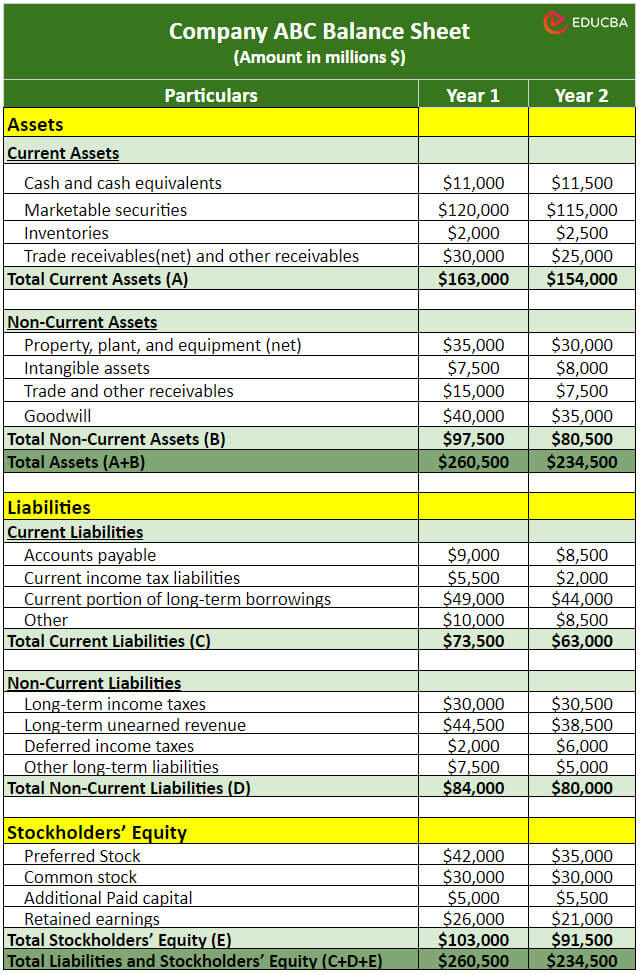
1. Vertical Balance Sheet
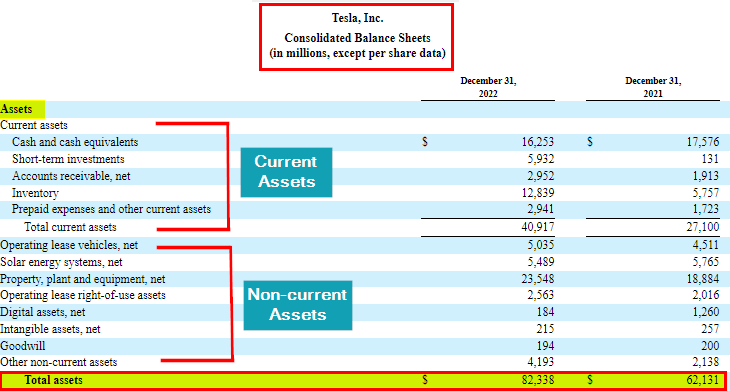
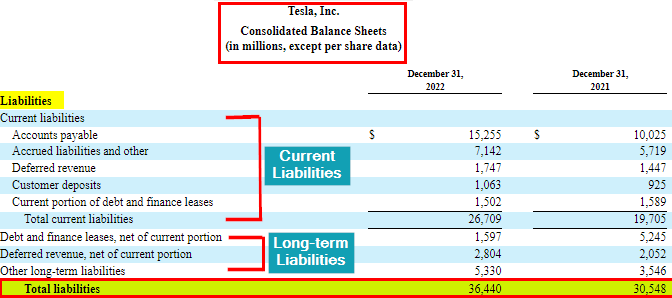
In a vertical format, the assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity are presented one above the other. It’s a common format businesses like Apple, Walmart, Tesla, etc., use to highlight the relative proportions of assets, liabilities, and equity in a clear and concise manner.
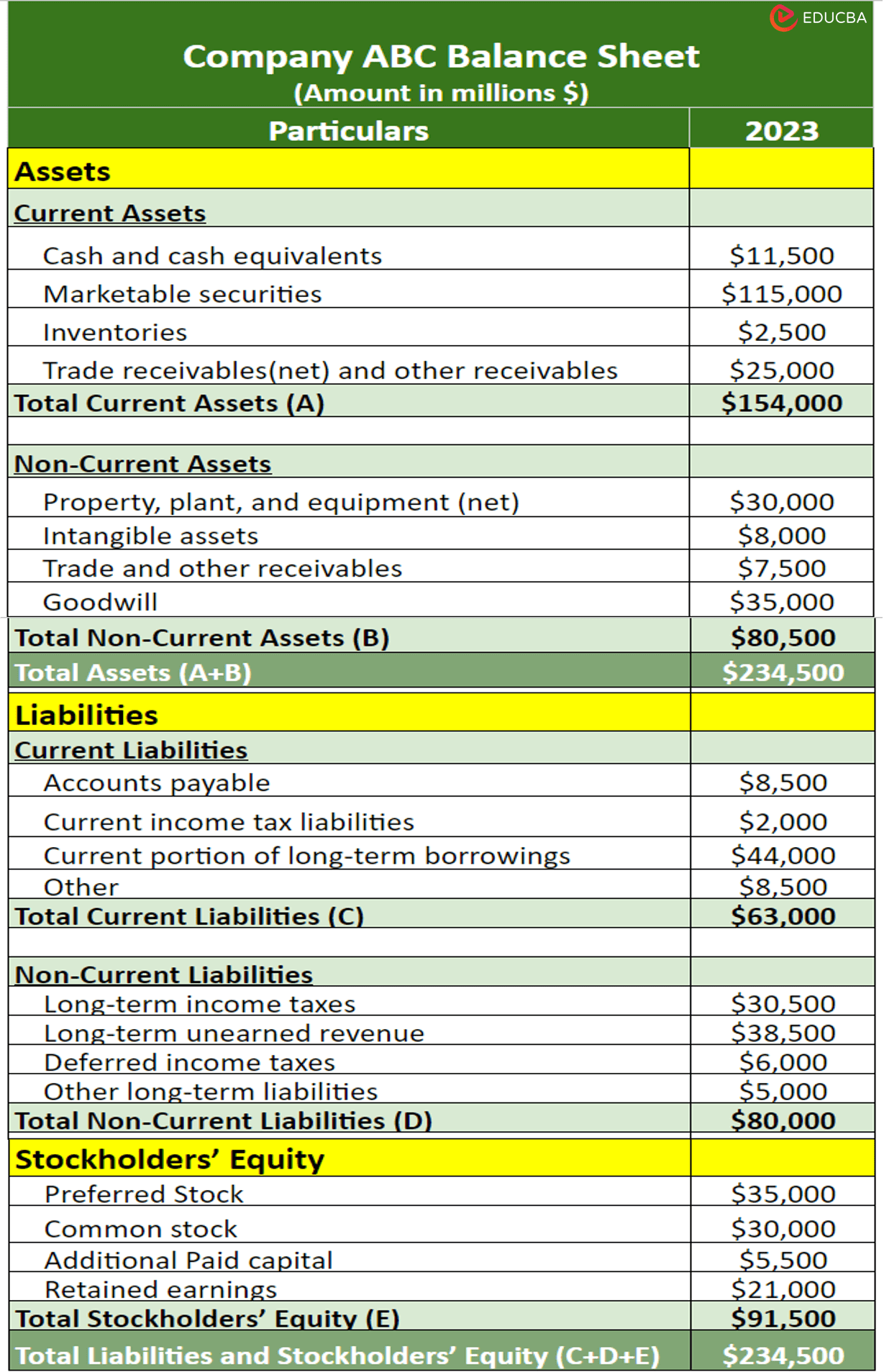
Vertical Balance Sheet Sample:
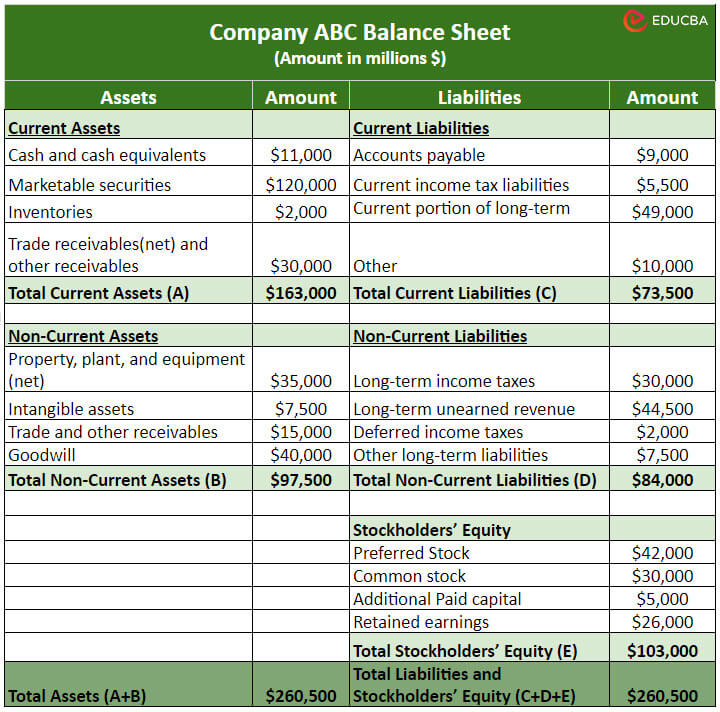
2. Horizontal Balance Sheet
In the horizontal format balance sheet, the financial information is present in a horizontal row-by-row format. This format allows for quick year-over-year comparisons as it is easy to identify changes in each category over time.
Horizontal Balance Sheet Sample:
Components
There are three main balance sheet components: Assets, liabilities, and equity.
1. Assets: Assets are what a company owns. Its two main types are current assets and non-current assets.
2. Liabilities: Liabilities represent what a company owes. Its two main types are current liabilities and non-current liabilities.
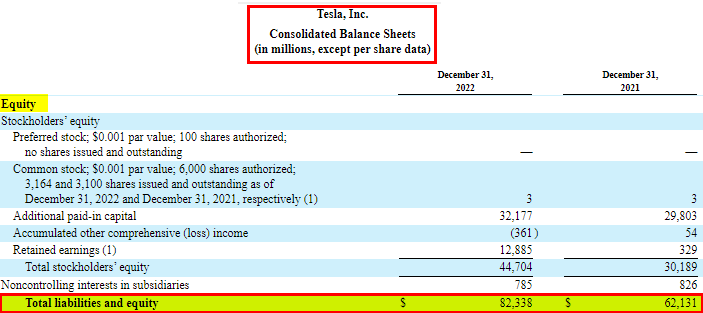
3. Equity: Shareholders’ or owner’s equity is the remaining interest in the company’s assets after deducting liabilities.
Real-Company Examples
Here, we are looking at a few real companies’ balance sheets.
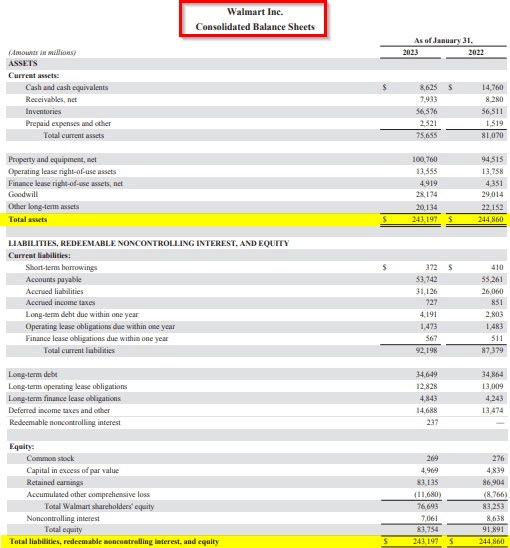
1. Walmart Inc.
Here is Walmart’s consolidated balance sheet for the fiscal year ending on January 31, 2022-2023. We can see their assets and liabilities balance out at $243,197 Million in 2023. Moreover, the assets have decreased from $244,860 in 2022 to $243,197 in 2023.
(Image Source: Walmart Annual Report 2023)
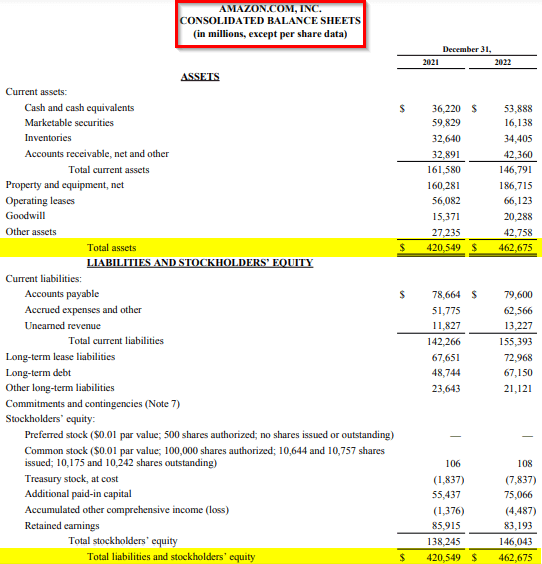
2. Amazon Inc.
Given is Amazon’s balance sheet for the years 2020-21 and 2021-22. The total assets and liabilities are in a balance at $462,675 Million in 2022. In comparison to the previous year, Amazon’s total liabilities and shareholders’ equity increased from $420,549 to $462,675 (10.03% increase).
(Image Source: Amazon Annual Report 2022)
How to Construct a Balance Sheet?
Let us cover how to prepare a balance sheet for a company.
1. Include the date (year) of the financials at the top, along with your company name. For instance, we are creating a balance sheet for Company ABC for the year 2023.
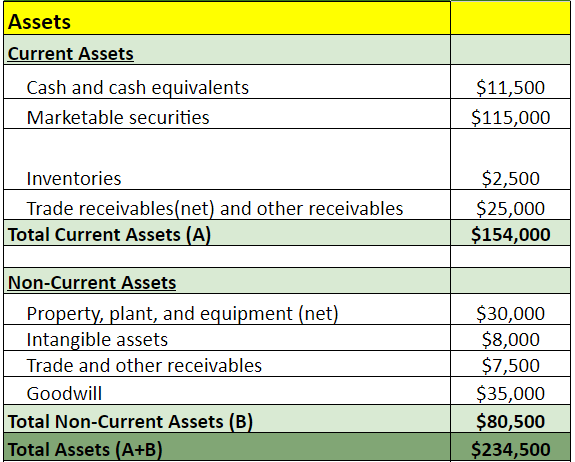
2. List all assets of the firm, including current assets (cash, accounts receivable, and inventory) and non-current assets (property and equipment). Then, find the sum of current, non-current, and total assets.
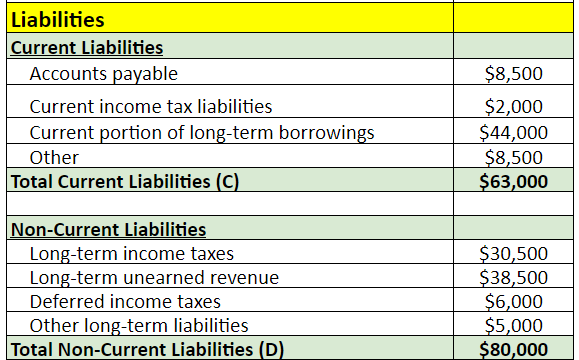
3. List all the company’s current liabilities (accounts payable and short-term debt) and non-current liabilities (long-term debt). Similar to assets, find the total current and non-current liabilities.
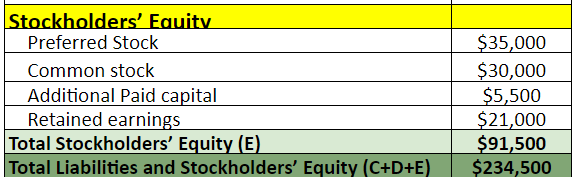
4. List all the shareholders’ equity items like common stock, retained earnings, etc. Find the total shareholders’ equity value and then add total current liabilities, non-current liabilities, and shareholders’ equity.
5. Ensure that the total assets are equal to the total liabilities & equity to balance the sheet.
6. Choose a preferable format and present the information in a structured manner with clear headings and categories. For example, we chose the vertical format.
7. Optionally, provide notes and disclosures to explain significant accounting policies, assumptions, and any other relevant information.
How to Read a Balance Sheet?
To read and understand a balance sheet, you first need to clearly understand all of the balance sheet items, like inventory, accounts receivable & payable, PP&E, debts, goodwill, etc.
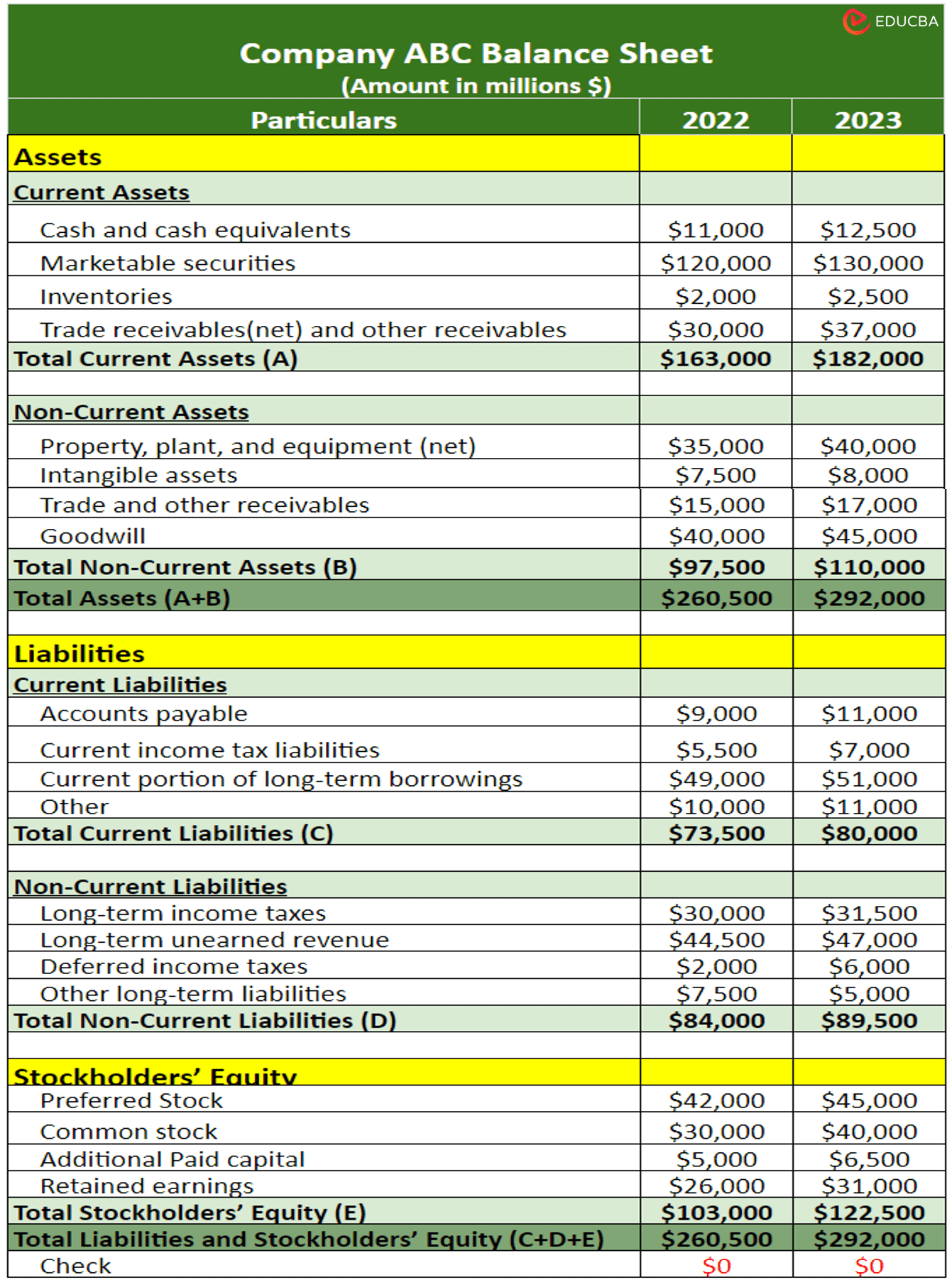
Here is how you can read a balance sheet step-by-step using this hypothetical sheet that we created in the previous example:
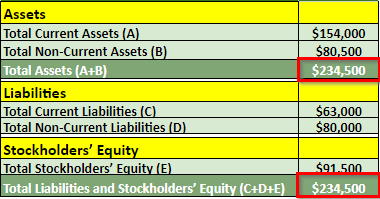
#1: Check all accounts: Assets, liabilities, and equity to understand how much the company has in debt, how much ownership the company has, and how much has the investors invested in the firm.
Example: In 2023, ABC Inc. has total assets of $292,000, while its liabilities and shareholders’ equity are $169,500 and $122,500, respectively.
#2: Use the balance sheet equation “Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders’ Equity” to ensure that the balances of assets and liabilities are in balance. And if they are not, find out the reason for the imbalance.
Example: When applying the equation for the year 2023, where ‘Assets ($292,000) = Liabilities ($169,500) + Shareholders’ Equity ($122,500)‘, we see that our sheet is in equilibrium.
#3: Calculate balance sheet ratios like current ratio, debt-to-equity, ROI, etc., to gain a deeper understanding of the company’s financial stability, solvency, efficiency, and profitability.
Example: Calculating the ratios for the year 2023 tells us that the company has good financial stability and moderate leverage.
⇒ Current Ratio = Current Assets/Current Liabilities = 2.28
⇒ Debt-to-Equity = Total Debt/Shareholders’ Equity = 1.38
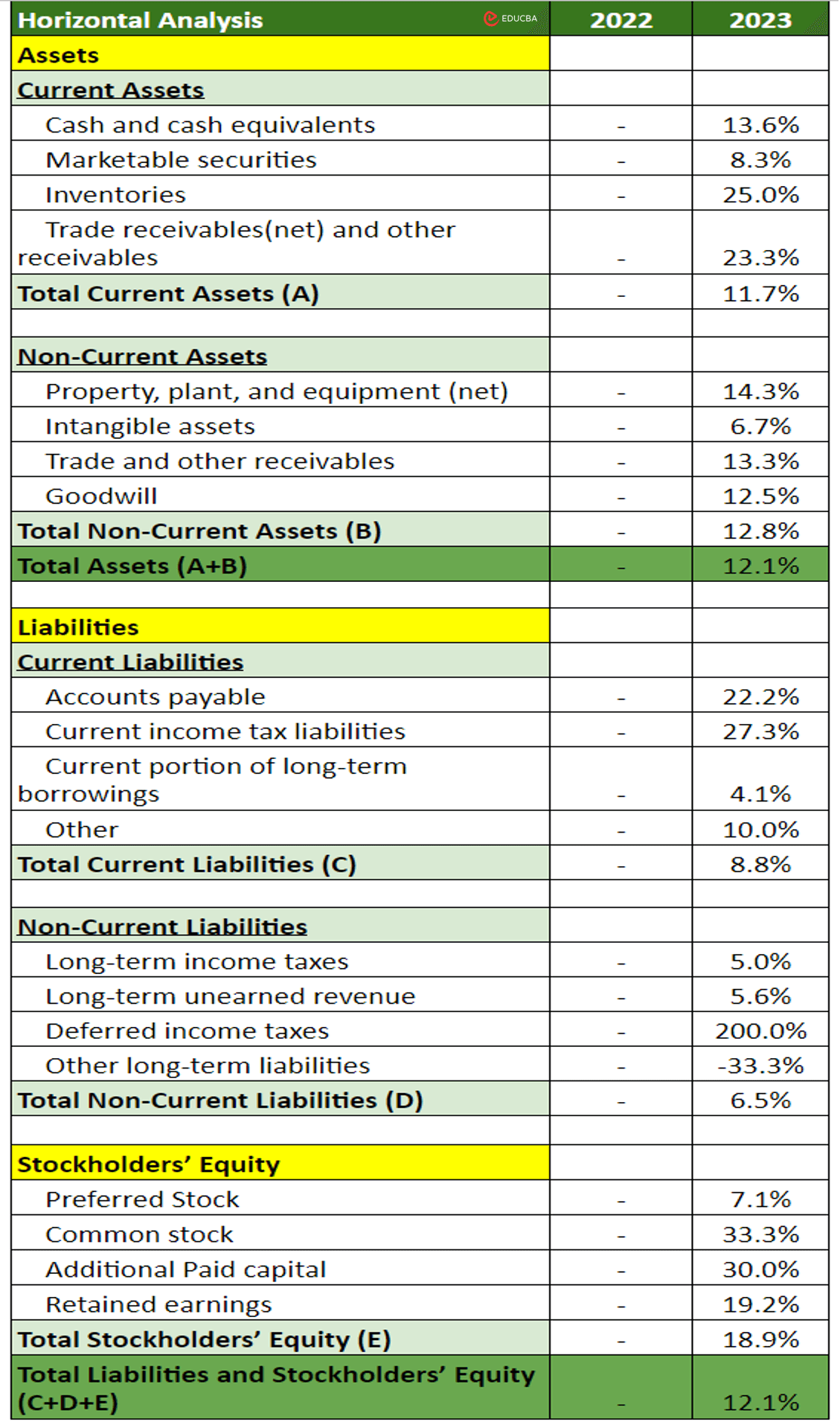
#4: Finally, perform an in-depth balance sheet analysis using horizontal analysis to compare the latest data with previous years’ information to find trends and patterns. This analysis involves calculating the percentage increase or decrease in each sheet item using the following formula:
Example:
Horizontal Analysis of Company ABC:
Furthermore, apart from the balance sheet itself, you can also locate the notes and disclosures to get a detailed knowledge of how the company manages and accounts for balance sheet items.
Importance
A balance sheet is important for various reasons mentioned as follows:
- It is one of the essential tools investors, creditors, and shareholders use to understand the business’s financial health. It helps to determine the business’s financial position at any time.
- It tells us the structure of the assets and liabilities of the company. This helps analysts calculate various financial ratios to understand the company’s health.
- Potential acquirers use it to identify any non-essential or redundant assets during acquisition.
- It can tell investors if the company is capable enough to pay dividends.
- It is a crucial document banks require to approve a business loan.
- We can determine the company’s growth rate by comparing it for several years.
- We can use it to determine whether a company funds its operations from its profit or debt.
Limitations
- It doesn’t capture off-balance sheet items. For instance, it only considers the acquired assets and not the internally developed ones.
- It is easy to manipulate or misrepresent information as the management may choose a profitable period to create a balance sheet. Thus, it may not reflect the actual market value.
- It offers a limited historical perspective, unlike income and cash flow statements, which are crucial indicators of a company’s growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. Which account does not appear on the balance sheet?
Answer: In simple terms, any temporary accounts, like revenue, expenses, profits, etc., do not appear on the balance sheet. These are off-balance sheet items that the company uses but do not add to the quarterly or annual report.
Q2. Who prepares the balance sheet?
Answer: Here are a few roles that are responsible for creating it:
- The company’s financial analysts and managers play a crucial role in collecting and organizing the financial data needed for the balance sheet.
- CPAs or CAs compile and audit it, ensuring that it adheres to accounting standards and accurately reflects the company’s financial position.
- Chief Financial Officers are key executives responsible for overseeing the company’s financial operations. They often have a significant role in preparing and reviewing the sheet before it is finalized.
- In many cases, external auditors are involved to independently review and verify the accuracy.
- In smaller businesses or startups, the business owner or a designated employee may prepare the balance sheet.
Q3. What’s the relationship between the balance sheet and other financial statements?
Answer: The balance sheet is linked to the income statement and cash flow statement. Together, these three financial statements give us a detailed view of a company’s financial performance. The income statement shows how the company performed over a period, while the cash flow statement tracks cash movements.
Q4. Why is the balance sheet important for investors and analysts?
Answer: The balance sheet is crucial for assessing a company’s financial health. It provides insights into a company’s liquidity, solvency, and overall stability. Investors and analysts use it to make informed decisions about investing in or lending to a company.
Recommended Articles
We are hoping you found this detailed guide on the Balance Sheet beneficial. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more,