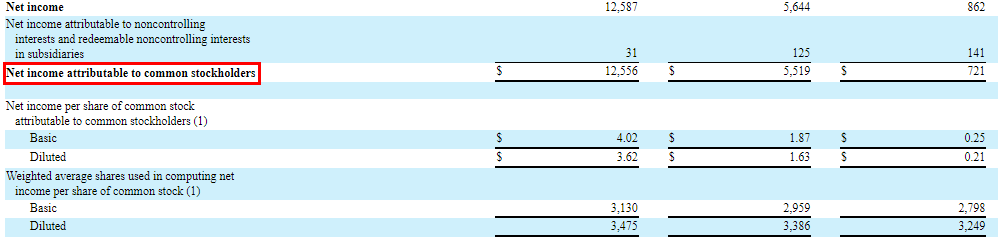Updated November 21, 2023
Income Statement Definition
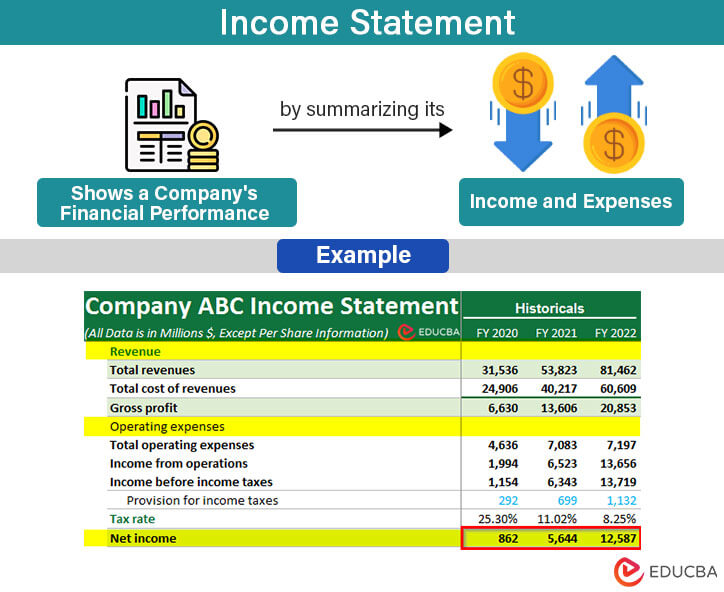
The income statement is a document that presents a company’s financial performance by showcasing its expenses and income for a specific period. For instance, a manufacturing company will create an income statement to showcase its expenses and revenue for the year 2023.
An income statement records the company’s revenue and expenses to calculate its profit and loss for the fiscal year. It reflects the profitability of the company by showing the gross profit and net profit earned during the year. It is crucial for an organization as it helps assess its performance and financial position. It is considered one of the three primary financial statements: balance sheet and cash flow statement. It is mainly prepared quarterly/annually and is present in the company’s annual report and other financial statements.
Table of Contents
- Definition
- Real-World Examples
- Format & Components
- How to Read it?
- How to Create it?
- Who Uses Income Statement and Why?
Real-World Examples
Here are some real-world examples of income statements from different industries:
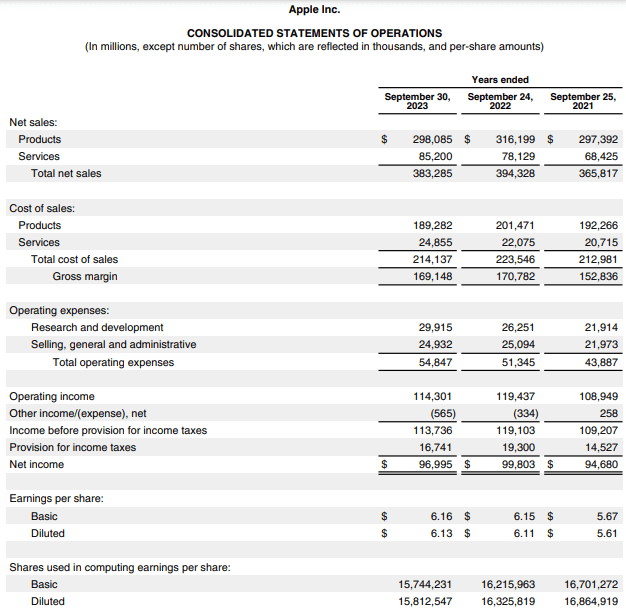
1. Apple
Here is Apple’s consolidated statement of operations, also known as the income statement, for the fiscal years ending on September 30, 2021-2023.
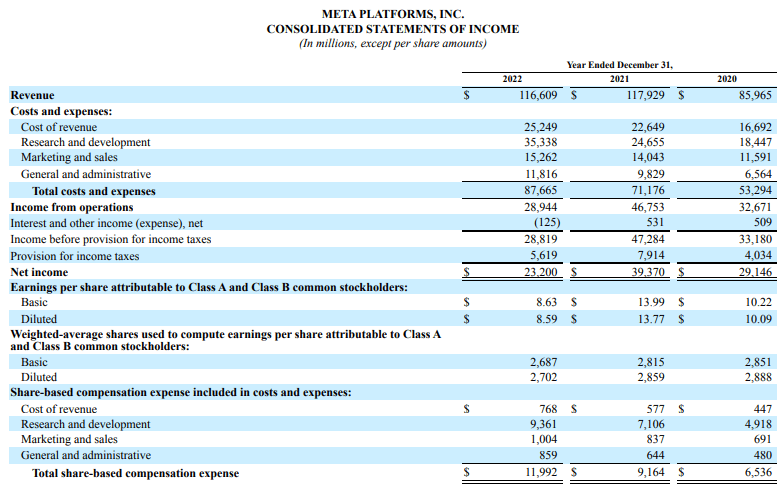
2. Meta Platforms
Here is Meta’s consolidated statement of income for the fiscal years ending on December 31, 2020-2022.
Format & Components
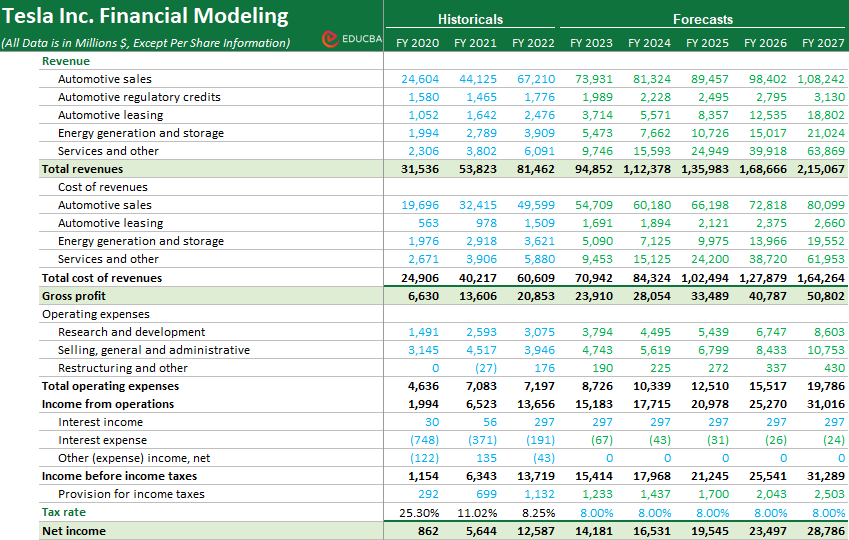
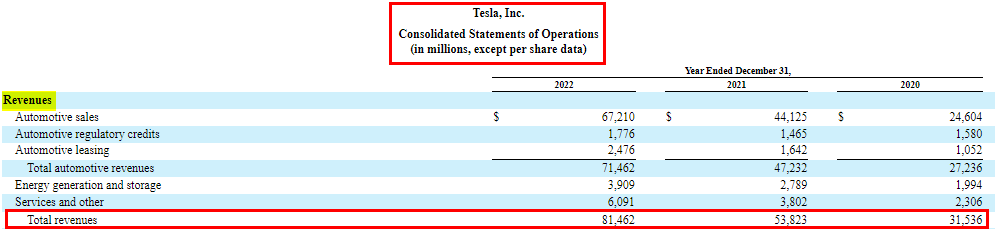
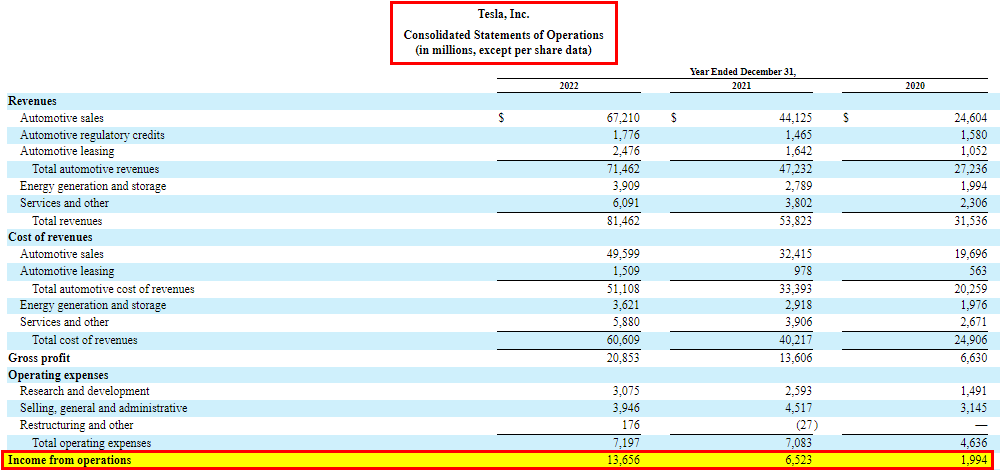
The below-given income statement format is from EDUCBA’s Financial Modeling Course on Tesla. It displays Tesla’s financial performance from fiscal years 2020 to 2022.
The main components of an income statement are:
1. Revenue
The top line of the income statement represents the total amount of money earned from selling goods or services. We can further break down revenue by product lines, geographic regions, or other relevant categories. Revenue is an important parameter that denotes the amount the organization can generate in its financial year.
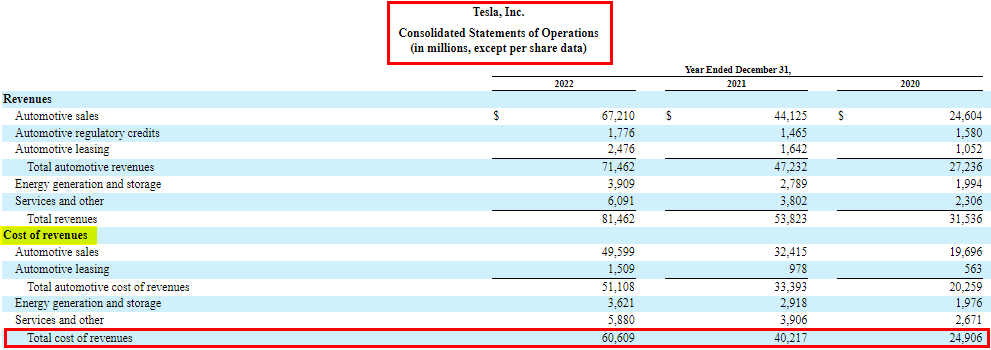
2. Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)/ Cost of Revenue
All costs directly related to producing the goods or services that businesses sell come under COGS, such as labor, raw materials, etc.
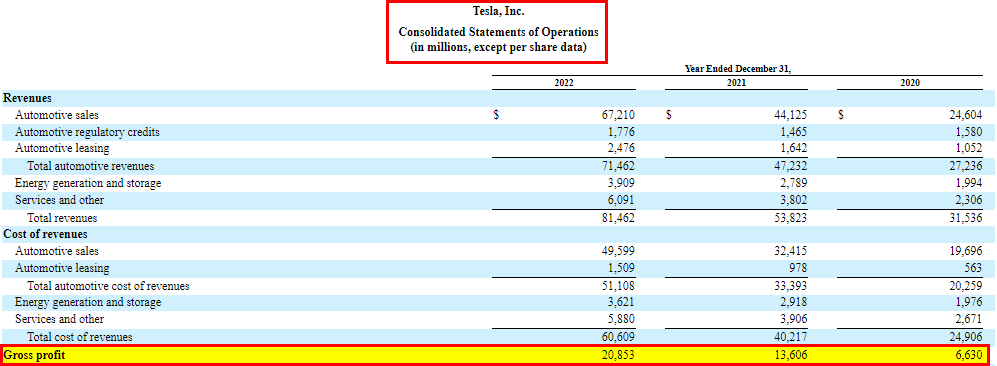
3. Gross Profit
Companies subtract the cost of goods sold from their total revenues to find a gross profit. It’s important to measure a company’s profitability before accounting for other operating expenses.
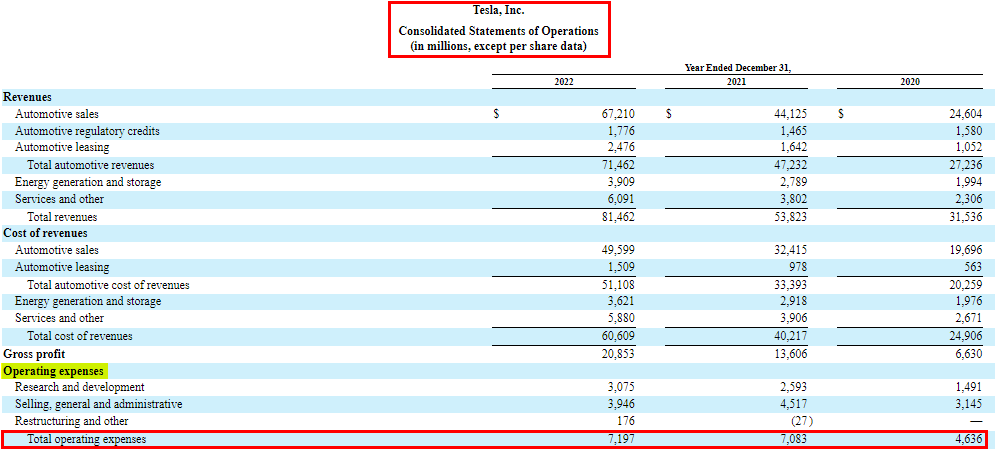
4. Operating Expenses
All expenses a firm incurs for their day-to-day operations, like utility, rent, salary, etc., come under operating expenses.
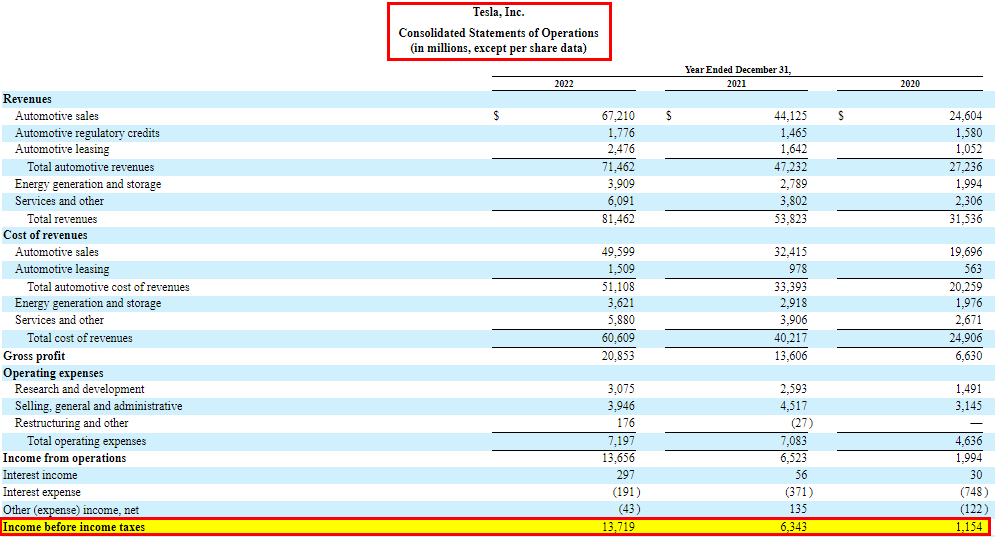
5. Operating Income/Income from Operations
Firms compute operating income by subtracting operating expenses from gross profit. It represents the profit derived from the core operations of the business.
6. Income Before Taxes
It is the company’s income before accounting for income taxes. It’s calculated by adding operating income and other income and subtracting other expenses.
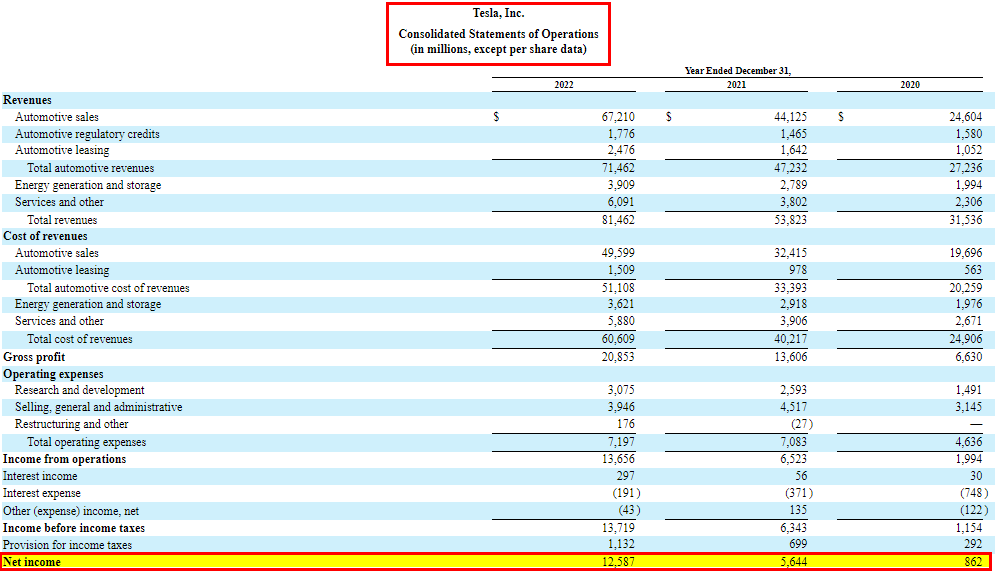
7. Net Income
Net income represents the company’s profit/losses after all expenses, including income taxes, have been deducted. It’s often called the bottom line because it shows how much money the company has earned or lost during the reporting period.
8. Earnings Per Share (EPS)
This figure is often reported alongside net income and represents the portion of a company’s profit allocated to each outstanding share of common stock. It is a key metric for investors.
How to Read an Income Statement?
To read and understand an income statement, you must thoroughly understand its components. As we discussed all its components, let’s understand how to read each of Tesla’s income statement components.
1. Revenue
To understand the revenue section, just identify the major revenue sources of the company. For instance, if you consider Tesla, you can see that significant sources of revenue are Automotive sales, Automotive regulatory credits, Automotive leasing, Energy generation and storage, and Services and others.
After that, you can compare the growth of each segment from one year to the next. It means finding out how much the revenue increased compared to the previous year. For example, in 2022, Tesla saw significant growth in different areas of revenue.
- Automotive Sales: Surged by 52.3% to $67.2 million.
- Automotive Regulatory Credits: Increased by 21.2% to $1.8 million.
- Automotive Leasing: Grew by 50.3% to $2.5 million.
- Energy Generation and Storage: Revenue increased by 40% to $3.9 million.
- Services and Other: Grew by 60.1% to $6.1 million.
2. Cost of Revenues
In the cost of revenue section, we look at the expenses directly as a percentage of sales (revenue). For Tesla, these costs include:
- Automotive Sales: 74% of sales in 2022 and 73% of sales in 2021.
- Automotive Leasing: 85% of sales in 2022 and 67% of sales in 2021.
- Energy Generation and Storage: 93% of sales in 2022 and 105% of sales in 2021.
- Services and Other: 97% of sales in 2022 and 103% of sales in 2021.
3. Operating Expenses
Similar to the cost of revenues, operating expenses are directly compared with sales. For instance, you can find their percentage of sales or also understand their increase or decrease as compared to the previous year as follows.
- Research and Development: Tesla invested $3.1 million in R&D in 2022, up 18.7% from 2021.
- Selling, General, and Administrative (SG&A): SG&A costs reduced to $3.9 million in 2022, down 12.4% from 2021.
- Restructuring and Other: Expenses changed from -$27 million in 2021 to +$176 million in 2022.
4. Interest Income
To read this, note the increase from $56 million in 2021 to $297 million in 2022. This rise signals higher returns on investments or interest-bearing assets, indicating improved income from cash reserves or investments.
5. Interest Expense
In 2022, interest expenses reduced from $371 million to $191 million. This drop suggests Tesla managed to lower its borrowing costs, resulting in cost savings related to debt financing.
6. Other (Expense) Income, Net
Tesla’s other income and expenses shifted from a positive $135 million in 2021 to a negative $43 million in 2022. This change indicates fluctuations in non-operating income and expenditures, possibly due to various financial activities or external factors.
7. Provision for Income Taxes
The provision for income taxes increased from $699 million in 2021 to $1,132 million in 2022, a 62.2% growth. It indicates a higher tax liability for the company, likely due to increased profitability.
8. Tax Rate
Tesla’s tax rate decreased from 11.02% in 2021 to 8.25% in 2022. A lower tax rate signifies efficient tax planning or the use of tax incentives, contributing to higher after-tax profits.
9. Net Income
Tesla’s net income surged from $5,644 million in 2021 to $12,587 million in 2022. This substantial growth showcases the company’s ability to generate more income after accounting for taxes and other expenses.
How to Create a Basic Income Statement?
Follow these steps to create a basic income statement:
Step #1: Select the period for which you want to create the income statement.
Step #2: Generate the Trial Balance Report for the period you selected.
Step #3: Determine the total revenue for the period by adding up all income from the sale of goods or services. Make sure also to include the money that you are yet to receive.
Step #4: Determine the cost of goods sold for the period.
Step #5: Determine the Gross Profit.
Step #6: Determine the company’s operating expenses, which are expenses the company incurred during its normal business course.
Step #7: Determine non-operating expenses and the company’s non-operating income, which are the expenses/income of the company from sources other than normal business operations.
Step #8: Determine the Net Income for the company.
Step #9: Report all the calculated values on the income statement.
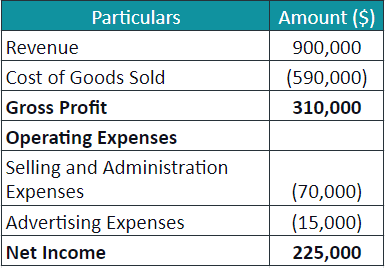
Example:
We have the following data for ABC Ltd for the year 2023. Let us create an income statement for them.
- Revenue = $900,000
- Purchases = $600,000
- Manufacturing expenses = $20,000
- Direct labor costs = $70,000
- Selling and Administrative costs = $70,000,
- Advertising expenses = $15,000
- Closing Inventory = $100,000.
Solution:
As we know the revenue, we skip to the second step to calculate the COGS as,
The cost of Goods Sold is calculated as follows,
= $600,000 + $20,000 + $70,000 – $100,000 = $590,000
Who Uses Income Statement and Why?
The primary users and uses of the income statement include:
| Used by | Purpose |
| Investors & Shareholders | To evaluate a company’s profitability and its ability to generate returns. They often look at metrics like earnings per share (EPS) to assess the company’s financial health and growth potential. |
| Creditors & Lenders | To examine a company’s ability to generate sufficient cash flow to cover its debt obligations. They want to ensure that the company can make interest payments and repay the principal on loans. |
| Government & Regulatory Agencies | To verify tax liabilities and ensure compliance with accounting and reporting standards. |
| Management & Executives | To monitor and manage the company’s operational performance. It helps them make informed decisions about cost control, revenue generation, and profitability improvements. |
| Potential Business Partners | To understand the financial health and performance of the target company when considering partnerships, joint ventures, or mergers and acquisitions. |
| Internal Stakeholders | To understand how the company’s financial performance affects its ability to provide compensation, benefits, and future growth. |
| Competitors | To gain insights into the business’s strategies, strengths, and weaknesses. |
| Analysts and Financial Experts | To analyze trends, make forecasts, and compare its performance to industry benchmarks and competitors. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1. What are the limitations of income statements?
Answer: The following are a few limitations of income statements:
- Accrual Accounting: Companies usually prepare it based on accrual accounting, which may not reflect actual cash transactions. It can potentially lead to discrepancies with the cash flow statement.
- Cash Flow Vs. Sales: Representation of sales on credit might not be accurate in the profit and loss statement, as they only reflect when cash is received.
- Potential Manipulation: Management may use accounting rules to manipulate these statements to present a favorable picture to stakeholders.
Q2. How can we use an income statement to assess a company’s finances?
Answer: We can assess a company’s financial stability and future prospects by analyzing key financial ratios and trends on the income statement. It usually includes evaluating the profit margins, revenue growth, expense control, etc.
Q3. What are single-step and multi-step income statements?
Answer: A single-step income statement has a single heading for total income and total expenses. There is no separate heading for operating and non-operating costs and income. This format is common among small businesses.
On the other hand, a multi-step income statement calculates the net income in multiple steps. There is a separate step for calculating gross, operating, and net profit. This method is more useful when companies want to calculate various ratios and perform comparisons.
Recommended Articles
We hope you found this comprehensive article on Income Statement helpful. For similar articles, please refer to the following.